
GROßE KRUEZER
The Big Three - SMS Derfflinger, Lützow, and Hindenburg
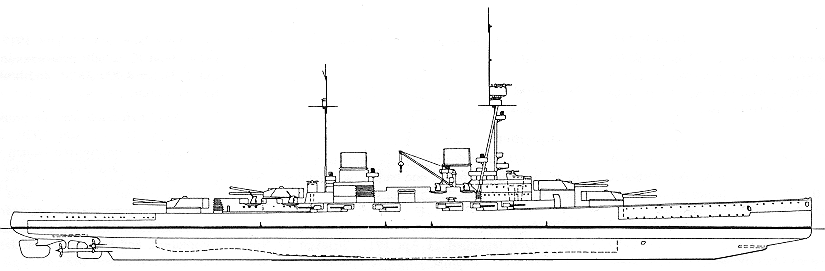
Laid down in 1912, SMS Derfflinger was a complementary design to the battleship SMS König. Both mounted their main battery in twin turrets on the centerline and both classes were outfitted with a partially oil-fired boiler arrangement. Derfflinger was the first German capital ship to have a flush deck design, while the lack of secondary casements mounts in the hull itself presaged the turn naval design would take in the 1930's.
SMS Derfflinger and her newly commissioned sister-ship, SMS Lützow, were active at Jutland, and between them they are credited with sinking and/or assisting in the sinking of HMS Invincible and HMS Queen Mary. Lützow took over 24 hits, including four 15" shells, but still made it all the way back to the entrance of the Kiel Canal only to find that, with 7,500 tons of water in her she could not get over the sandbar at the entrance to the estuary, so she was abandoned and sunk by an escorting torpedo boat, G38. Derfflinger, with 17 heavy and 4 medium hits plus 3,000 tons of water aboard, limped home while trying not to foul her propellers on the loosened anti-torpedo nets trailing along her side.
Originally fitted with straight pole masts, during repairs following Jutland Derfflinger (and Hindenburg while whe was being built) was fitted with a tripod mast in place of her foremast, and had several 8.8cm guns removed. Also, as a result of the Jutland experience, anti-torpedo nets were removed from all combatants.
Delayed by other construction priorities and built to a modified Derfflinger design, SMS Hindenburg commissioned
too late to see Jutland. She was the fastest of the three, coming in at 26.6 knots (combat load), but never saw combat. She holds two distinctions:
1) Last battlecruiser completed for the Imperial German Navy
2) Last ship to sink during the Grand Scuttle at Scapa Flow.
Derfflinger and Hindenburg survived the war to be interned at Scapa Flow, where they both were scuttled on June 21, 1919. Though they were the last battlecruisers completed by the German navy, they were not the last built - that claim belongs to the Mackensen class.
PHOTOS

SMS Derfflinger

SMS Lützow

SMS Hindenburg
SPECIFICATIONS
Project Name: Heavy Cruiser K (Derfflinger) | Ersatz Augusta (Lützow) | Ersatz Hertha (Hindenburg)
Builder: Blohm & Voss, Hamburg | F Schichau, Danzig | Imperial Dockyard, Wilhelmshaven
Laid Down: March 30, 1912 | July ?, 1912 | October 1, 1913
Launched: July 12, 1913 | November 11, 1913 | August 1, 1915
Commissioned: September 1, 1914 | August 8, 1915 | May 10, 1917
Sunk: Derfflinger and Hindenburg - June 21, 1919 (scuttled at Scapa Flow) | Lützow - May 31, 1916 at Jutland |
Scrapped: Derfflinger - Raised 1939, Scrapped 1956 | Lützow - partially broken up in-situ 1961-1962 | Hindenburg - Raised July 22, 1930, Scrapped 1931-1932
Displacement: Derfflinger/Lützow - 26,600 tonnes (designed) / 31,200 tonnes (maximum) | Hindenburg - 26,947 tonnes (designed) / 31,500 tonnes (maximum)
Dimensions (meters): Derfflinger/Lützow - 210.4 (overall) x 29.0 x 9.56 | Hindenburg - 212.8 (overall) x 29.0 x 9.57
Dimensions (feet): Derfflinger/Lützow - 694.32 (overall) x 95.7 x 31.55 | Hindenburg - 702.24 (overall) x 95.7 x 31.58
# of Shafts/Propellers: 4
# of Propeller Blades: Derfflinger/Lützow - 3 (3.9m diameter) | Hindenburg - 3 (4.0m diameter)
# of Rudders: 2 (tandem - one ahead of the other on the centerline)
Max Speed/Range: Derfflinger/Lützow - 26.5 kts / 5,600 nm at 14 kts | Hindenburg - 26.6 kts / 6,100 nm at 14 kts
Main Battery: Eight 305mm (12")/50 caliber - 4 dual turrets
Secondary Battery: Derfflinger - Twelve, Lützow/Hindenburg - Fourteen 150mm (5.9")/45 caliber - all single casement mounts
Anti-Torpedo Boat / Anti-Aircraft Battery: Twelve 88mm (3.5")/45 caliber (After 1916 only two carried by Derfflinger, four by Hindenburg) - single mounts
Torpedo Tubes: Four 50cm tubes (all underwater - one bow, one portside firing astern, one mounted on each side just forward of "Anton" turret)
Complement: 44 officers and 1068 enlisted (as designed) / 1,390 (wartime)
LINKS TO OTHER WEB-SITES
Naval Weapons of the World German Naval Guns
Naval Weapons of the World Pre-World War II German Torpedoes
German Kriegsmarine Encyclopedia
The Imperial German Navy from 1888 to 1918
Back to Großen Kruezers.
Back to Home.